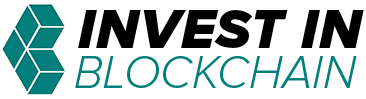Nxt is an OG of the crypto world. Founded in 2013, Nxt is a completely open-source payment network that was originally conceived as a flexible platform on which to build applications and financial services.
According to Wikipedia:
Nxt is a ‘second generation’ blockchain platform that builds on and enhances the basic functionality of pioneering cryptocurrencies like bitcoin and ethereum.
Nxt came about for a simple reason: its developers wanted to experiment with new technology and expand the number of things people could do on the blockchain.
What’s Unique About Nxt?
In a way, Nxt represents the natural evolution of blockchain technology. Bitcoin broke the trail, and behind it many different versions forked or incarnated themselves. But Nxt is different and was written completely from scratch in Java.
Nxt was conceptualized to build applications directly onto the blockchain. Frequently compared to Ethereum, it was the first blockchain to introduce a Proof-of-Stake consensus protocol with no need for energy-intensive mining.
One of the main differentiators of Nxt is that it has more restrictive components and APIs in creating blockchain applications, and it claims to be “more secure from hackers and buggy codes”.
Along with its token (Nextcoin or NXT), Nxt gives project developers and individuals a powerful toolkit, combined with an easy-to-use system to create a feature-rich environment. A few of these features are a monetary system, data cloud, voting system, account control, authentication, third-party plugins, alias system, and asset exchange.
If you’re looking for key strengths, they’re not hard to find in Nxt. The network has been running for almost 4 years, and at the time of press, the NXT token has a market cap around $430 million. Nxt also has a large community of fanatical followers, a solid foothold in the business world, and a strong development team (both core and third-party).
Nxt cuts out the middleman and allows access to the world of decentralized exchanges and trading. It also allows for the creation of digital assets, makes crowdfunding easier, and provides the ability to use NXT’s in-built authentication tools.
Nxt also offers up a simple and easy-to-use entry point into blockchain. Nxt’s unique set of modular features are flexible and allow developers to build things easily. Nxt has an extensive wiki, a helpdesk, and dedicated developers who are said to be responsive to queries.
In the future, Nxt will be linked to Ardor and its child chain Ignis (more on this below).
A Short History of NXT
On September 28, 2013, a Bitcointalk.org member going by the name BCNext created a forum thread announcing the proposed launch of Nxt as a new-generation cryptocurrency. BCNext remains anonymous, just like Satoshi, but there are has been a lot of speculation as to who he or she is.
A white paper was released in support of the project, and, following that, BCNext held the ICO for Nxt. It was one of the first ICOs in crypto, with a total of about 21 BTC collected in late 2013. At the time, this was worth around US$6,000.
Despite this inauspicious start, the future for Nxt proved relatively bright.
Toward the end of 2013, fundraising efforts concluded and the genesis (1st) block was published. 1,000,000,000 coins were distributed to 73 stakeholders in proportion to their level of contribution to the project. In April 2014, the full source code was released, and since that time a slew of other developers and collaborators have pitched in (for those interested, here is a good book about the early days of Nxt).
The core developers of Nxt eventually incorporated themselves as Jelurida, a startup based in the Netherlands. They hold the IP rights to the technology and have been working to develop it ever since. As work continued on Nxt, increasingly creative solutions were needed for the problems presented to developers. Jelurida subsequently made the decision to create an evolution of Nxt, called Ardor.
One key area where Ardor has improved on the Nxt protocol is the development of the parent-child architecture. The parent chain is responsible for processing and network security, while the child chains maintain operational functions that are important to the success of a cryptocurrency. Ardor is meant to be an elegant complement to Nxt, and the plan is for them to coexist, not for Ardor to completely replace Nxt. Ignis is the first child chain on the Ardor blockchain, and helps address bloat issues by allowing data to be “pruned” away on a preset schedule. For further explanation, check here.
All of this change obviously has ramifications for any holder of NXT.
Last year, Ardor tokens were distributed via a snapshot mechanism to holders of NXT. On December 28, 2017, Ignis was airdropped at 0.5 IGNIS for every 1 Nxt token that is held by the user. Upon the launch of the Ardor mainnet on January 1, 2018, the Ignis token has been made available for use within the Nxt Wallet.
Here is the roadmap for some of this evolution we’ve just described and a link to a comparison chart.
The Nxt Team
Nxt’s parent company, Jelurida B.V., is managed and run by a small team in Holland. Here are the key faces.

Lior Yaffe is the co-founder, managing director, and senior developer at Jelurida. He “eats and drinks programming and technology”, an interest that he’s had since his teenage years. Yaffe is the public face of Jelurida.

Kristina Kalcheva co-founded the company along with Yaffe and serves as both the managing director and chief legal counsel. She is an expert in licensing models and has spent years studying the legal challenges that arise from various blockchain use cases.
 Petko Petkov, co-founder and core developer, has a BSc in Informatics and an MSc in Electronic Governance. He also has some serious development chops, being proficient in Java, C++, Java for Android, JavaScript, Java SE, and Python.
Petko Petkov, co-founder and core developer, has a BSc in Informatics and an MSc in Electronic Governance. He also has some serious development chops, being proficient in Java, C++, Java for Android, JavaScript, Java SE, and Python.
 Tomislav Gountchev is the lead software architect at Jelurida. Gountchev comes from a decorated academic background, with a PhD from Berkeley and a BA from Cambridge University. He subsequently worked as a software engineer in Silicon Valley with a few notable companies (NextTag, eBay), founded nabble, and worked as an R&D software engineer for an open-source enterprise software firm.
Tomislav Gountchev is the lead software architect at Jelurida. Gountchev comes from a decorated academic background, with a PhD from Berkeley and a BA from Cambridge University. He subsequently worked as a software engineer in Silicon Valley with a few notable companies (NextTag, eBay), founded nabble, and worked as an R&D software engineer for an open-source enterprise software firm.
Outside the official team, an anonymous user going by the name JeanLucPicard is also credited as being a core developer. There are quite a few other developers active in the Nxt slack channel as well.
Lastly, we have the Nxt Foundation. The Nxt Foundation is a nonprofit organization also based in the Netherlands, run by community members to promote the use of the Nxt blockchain (also the blockchain of Ardor/Ignis). This is a separate entity from Jelurida, but since 2014 the foundation has been the point-of-contact for businesses and organizations interested in using these technologies, and it played a role in their development as well.
Challenges and Criticisms for Nxt
There are numerous question marks surrounding Nxt, namely, is it being sidelined in favor of newer tech? We’ll discuss this at length in the next section, but there are some other issues worth noting.
Since Nxt had no mining phase, all initial units were released to 73 people through a one-time fundraiser via bitcoins, after the announcement of the NXT project in the bitcointalk-forums by BCnext. Combine this with a PoS approach, and you have a situation where the big guys run the table.
At one point, the Nxt community had a very public spat with Bitcoin developer Jeff Garzik. Garzik took issue with the Nxt marketing approach, its anonymous developers, and their responses to constructive criticism. Nxt responded to some of these claims, of course, but it remains one of the more controversial moments in its history.
Another key problem the Nxt network ran into (like so many others) was blockchain bloat. Nodes get weighed down by the onerous task of having to store every transaction on the Nxt blockchain. This was one reason (among others) why Ardor/Ignis came into existence.
How to Purchase and Store NXT
Here is a list of wallets that hold NXT, many of which are also compatible with ARDR.
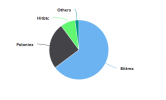
As the graph below indicates, NXT trading is dominated by a few exchanges, Bittrex and Poloniex primary among them. For a step by step guide on how to buy NXT, click here.
What’s Next for Nxt?
Jelurida is breaking new ground as they attempt to solve blockchain scalability problems through their use of child chains. But with the advent of Ardor and Ignis, the future of Nxt remains as uncertain as ever. Reddit has apprehensively been discussing what’s going to happen.
Nxt has been declared dead or dying more than a few times. But Jelurida has pushed back hard on this point:
Why would Jelurida stop developing NXT, a stable and mature product with a huge potential? NXT is our bread and butter. Rest assured my friends, NXT has a bright future, it has been around for almost 4 years and will be around for a long time.
It should be noted that this quote is from an article published in August 2017, and a lot of water has passed under the bridge since then. The price and market cap of the NXT token has dropped considerably YTD.
But there was also some good news at the end of the year.

The announcement of a deal like this is a positive indicator for any blockchain. But the consensus still appears to be that Nxt is gradually getting abandoned, or will go into years of slow decline. Finding people truly bullish on Nxt is not all that easy.
More time is needed to see whether development continues or whether things well and truly dry up. To stay current on all things Nxt, you can follow along on Twitter, keep tabs on Yaffe’s Medium blog, or join the Reddit community.