There are 2,099 cryptocurrencies listed on CoinMarketCap at the time of writing. While many won’t make the long-term cut, a handful represent companies with an earnest appreciation for blockchain technology.
These companies are building virtual mechanisms aiming at the long-term success of the crypto industry, and one of the biggest obstacles (aside from lack of awareness) standing in the way of mass adoption is establishing a secure way to decentralize a scalable ledger.
Some of the most prominent projects looking to solve this issue are Ethereum, EOS, NEO, and Cardano, who have all carved out a spot within the top 10 cryptos in terms of marketcap. Since crypto is mostly an enormous open-source project, blockchain startups are able to read into existing solutions and build their own ideas off what they find.
IOST, the Internet of Services, is currently building their own solution for scalable cryptocurrency, and they’re doing so in a novel way. During their ICO in early 2018, the startup managed to raise $31.3 million from investors supporting their efforts to solve the scalability problem.
With all the options available, and many investors looking to place their bets on long-term winners, here are 3 reasons why IOST is worth watching.
1. IOST’s Technological Approach is Impressive
Most of what makes IOST a serious contender will be written into the code that supports their token. The details have been laid out in their technical whitepaper, and it’s quite a dense read, but here are brief explanations of the main components.
Proof-of-Believability (PoB)
Perhaps one of the most intriguing features of IOST is their approach toward a secure, scalable consensus algorithm. Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus algorithms aren’t inherently scalable due to their growing size.
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) algorithms introduce the threat of centralization, because the more tokens you have staked, the more rewards you earn, which passively funnels money towards the wealthy.
IOST will implement Proof-of-Believability (PoB) in the attempt to ensure a decentralized block verification process that can be scaled to support 100,000 transactions per second. To accomplish this, PoB will separate all nodes on the their blockchain into 2 groups: believable and normal. This separation will initiate a 2-step verification process.
The first step focuses on high throughputs, while the second ensures honest decentralization. Believable nodes have the ability to verify transactions quickly. Next, samples of the “believably-verified” nodes will be validated by the normal nodes. By virtue of the normal nodes validation process, believable nodes are being rated during each transaction.
They receive a believability score based on a variety of factors, which are designed to ensure they’re acting honestly. If a normal node catches a believable node acting dishonestly, all tokens within the dishonest believable node will be transferred to a believable node with a better rating, and the dishonest nodes’ believability score drops to 0.
Efficient Distributed Sharding (EDS)
The term sharding is commonly brought up in discussions surrounding the scalability problem. Sharding theoretically allows for infinite scalability for blockchains by splitting node networks into smaller groups, which can then be verified concurrently, increasing the throughput of the system.
IOST will implement Efficient Distributed Sharding, which they describe in their whitepaper as:
A novel scheme to form shards that are both sufficiently large and strongly bias-resistant using a combination of DRP and a VRF-based leader election via cryptographic sortition.
The end result of EDS implementation equates to increased throughput in correlation with the increased number of nodes, while reducing resources dedicated to processing each transaction.
To prevent node issues from jeopardizing the system, IOST proposes the use of Algorand and Omniledger mechanisms to ensure that leading nodes use their Distributed Randomness Protocol (DRP). Failure to run the DRP leads to being excluded from network participation.
While sharding looks great on paper, and might perform well in lab-like conditions, the IOST team believes that additional preventative measures against malicious and faulty nodes are vital to the long-term success of any crypto venture looking to scale successfully.
In an effort to remain on the inventive edge of scalable blockchain solutions, IOST will implement 4 other unique protocols for Efficient Distributed Sharding: Distributed Randomness, TransEpoch, Atomix, and Micro State Blocks.
1. Distributed Randomness Protocol (DRP)
The IOST team concludes in their whitepaper that traditional means of generating randomness with Proof-of-Work or trusted beacons introduce “computational wastes and centralization concerns.”
To solve this problem, IoST will implement their Distributed Randomness Protocol, which is designed to meet a few requirements.
- The system must keep dishonest participation underneath a threshold that guarantees progress is being made without any adverse effects.
- The final number being generated is consistently random and unforgeable.
- Multiple participants acting dishonestly are unable to increase favorability during random number generation.
- A third party is able to verify the output and adheres to the rules listed above.
For more details, be sure to read through their technical whitepaper.
2. TransEpoch
Using the TransEpoch protocol allows groups of nodes to be switched in and out of shards, while allowing remaining nodes to continue their transaction validation process. This transitional phase can be looked at as a chink in the armor of IoST’s network.
By implementing the TransEpoch algorithm, Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) is maintained for each shard, preventing malicious nodes from taking over during the transition.
3. Atomix
While the TransEpoch protocol keeps the system secure during transitional phases, it doesn’t address the vulnerabilities that arise during inter-shard transactions. The Atomix protocol is short for the Byzantine Shard Atomic Commit protocol.
The design is a variant of the Omniledger algorithm, and it’s designed to prevent double spending attacks while maintaining transaction consistency between the ledgers of separate shards.
To summarize the process, if node x in shard X needs to send funds to node y in shard Y, the Atomix protocol will implement the following steps:
- Create a transaction inside shard X and let all nodes within that shard validate the transaction.
- Once all nodes in shard X approve the transaction, it is logged in X’s blockchain, while also locking the funds of node x into a UTXO message that’s sent to shard Y.
- The nodes of shard Y are then required to validate the transaction. If validated, node y will receive the funds.
- If the nodes fail to validate the transaction at any point during the process, funds are then sent back to node x.
4. Micro State Blocks (MSB)
Ensuring maximum security and immutability within blockchain networks is based on a fairly simple idea: make each node stores the entire blockchain. It doesn’t take a large number of transactions to guess what happens when there’s a large number of transactions; the network gets slower due to the increasing ledger size.
To minimize the time and resources required to create transactions on the chain, the IOST team is implementing Micro State Blocks, which their whitepaper calls “a novel mechanism to minimize the storage and bootstrapping costs for validators.”
With MSB implementation, the entire blockchain is distributed among multiple shards, and each shard is only required to store the previous block’s header — which is just enough information to identify a specific block.
2. The IOST Testnet is Promising
Most of what sets IOST apart from other smart contract-based solutions is baked into their software technology. In order to implement PoB and EDS effectively and securely over long periods of time, a whole host of protocols were introduced to support the ecosystem.
While building out a suite of software to support a project’s end goal is nothing new, the concept and implementation of a PoB consensus algorithm is novel to the industry. A common thread through IOST is their insistence on breaking their tasks down into realistically achievable pieces, then verifying the success and integrity each step of the way.
This thread stands true to the decentralized nature of blockchain technology as a whole, and proof of the team’s dedication has been logged on their extremely active GitHub page.
To get an idea of what’s different about IOST and their competitors, take a look at the details of their testnet release, Everest v1.0, compared to ETH and EOS.
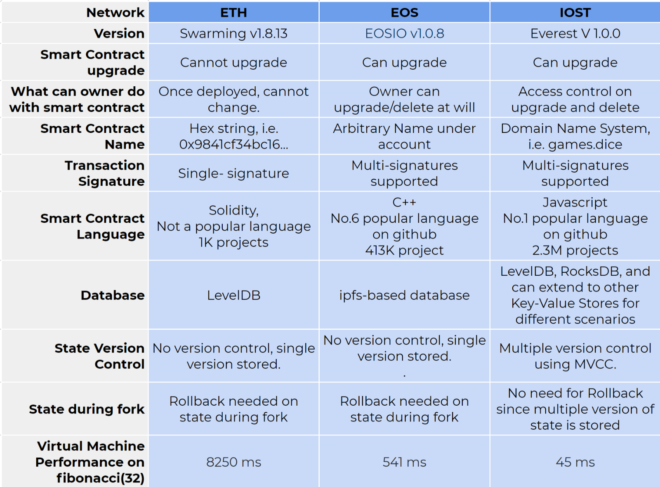
It’s a technically dense chart, but by taking some time to analyze it, the chart suggests even to laymen that IOST is looking to progress on the work laid down before them. In fact, the team has described their competitors as classmates looking to solve the same problem with their own approaches.
It’s also worth noting that IOST has managed to stay ahead of schedule. On the first iteration of their roadmap, their testnet was scheduled to launch in Q1 2019. Instead, the beginning of October 2018 marked the official launch of their testnet.
3. The IOST Team is Ahead of Schedule
Aside from the talented team behind IOST, a promising sign supporting their project is how well they’ve handled their proposed timeline. Compared to the many crypto projects who were unable to accurately predict their milestones, IOST is ahead of schedule, and recently released an updated roadmap.
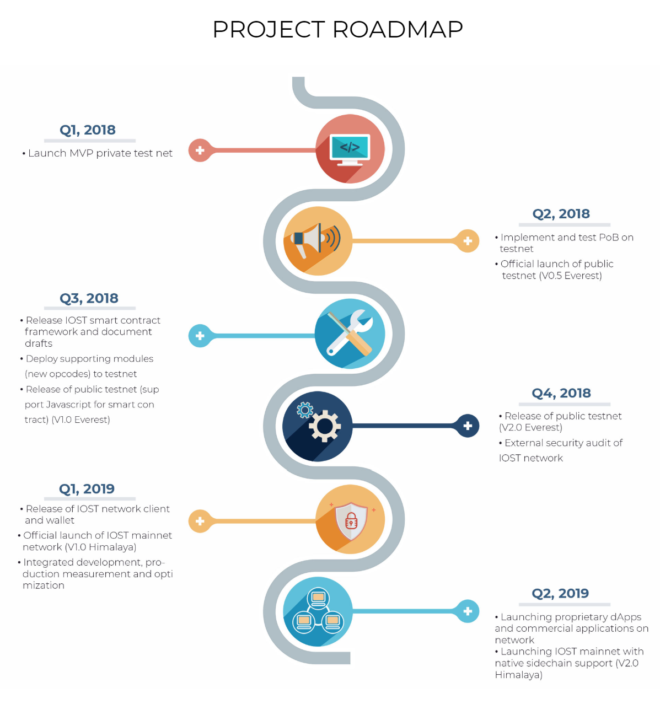
The original roadmap scheduled the release of their testnet, Everest v1.0, for Q1 2019, with the release of their mainnet scheduled for Q3 2019.
The new roadmap displayed above outlines the official launch of the IOST mainnet network during Q1 2019, with dapps, commercial applications, and sidechain support scheduled for Q2 2019.
IOST’s truncated roadmap could catch the eye, and respect, of developers currently deciphering which blockchain makes the most sense to build on top of. Nonetheless, opening the door to blockchain developers creates an exciting time for that ecosystem, and that time isn’t far off for IOST.
The IOST blockchain is backed by a qualified team and an extensive list of partners, setting the company up to contribute their technologic solutions to the industry at large. If they’re able to create a stable environment for developers and value for entrepreneurs, IOST will be standing on firm ground among its competitors.
To learn more about what IOST is bringing to the table, check out their website, follow them on Twitter, read their blog and Github page, and join them on Telegram and Reddit.