Have you ever wondered what would happen to our favourite cryptocurrency projects if a major component of the blockchain, such as the consensus mechanism, became obsolete? Unfortunately, the majority of our favourite cryptocurrency projects would be left scrambling as they struggle to adopt the latest technology. This is because traditional blockchains are not built with the future in mind.
However, if projects were to build on a highly flexible infrastructure that had the future in mind to begin with, such as QuarkChain 2.0, they would be at a serious advantage against their competition in implementing the new changes.
The team over at QuarkChain have developed a blockchain infrastructure technology that is extremely adaptable to the changing dynamics within the blockchain industry.
A Step Away From Infancy
The world of blockchain is still more or less in its infancy stage. At this moment in time, traditional blockchains still experience a huge gap between today’s capabilities and what is required for mass usage and adoption.
Blockchains today are typically very slow to confirm, and they experience extreme scalability problems. For example, Ethereum can only cater to 20 transactions per second (TPS), and when a large influx of users make transactions, leading to higher fees and longer confirmation times, it becomes congested (think back to the CryptoKitty fiasco).
QuarkChain 1.0 solved all of these issues, bringing blockchain out of its infancy stages, when it became the first blockchain to successfully implement state sharding. Sharding is a process that allows data to be horizontally partitioned, allowing many transactions to occur in parallel to each other. The process involves breaking down groups of subsets of nodes into shards, which then process transactions specific to that shard. This allows the throughput of the network to be horizontally scalable.
Ethereum and Ontology are both working on state sharding at this moment in time, and Zilliqa has managed to implement transactional sharding only.
With the use of state sharding, the QuarkChain blockchain managed to reach a TPS rate of 14,000, which is significantly higher than Ethereum’s 20 TPS. Furthermore, QuarkChain 1.0 also managed to maintain security, allow for scalability, and ensure decentralization of the network, all at the same time!
However, the development team at QuarkChain have decided to take things much further with the invention of QuarkChain 2.0.
Creating a Powerful and Usable Infrastructure
QuarkChain 2.0 aims to build a flexible, scalable, and user-orientated blockchain infrastructure solution through the use of sharding technology. They have already built an infrastructure for projects to start their blockchains on, which allows projects to build scalably in addition to being adaptable for the future. The emphasis on QuarkChain 2.0 is on the flexibility side of the blockchain.
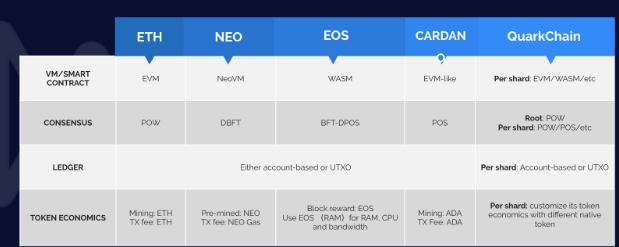
All public blockchains today, whether they use sharding or not, are bound by a combination of 4 components that create their network. These components include:
- The consensus mechanism – Whether it be proof-of-work, proof-of-stake, or delegated proof-of-stake.
- The transactional model – Bitcoin uses a script-based transaction model. Other projects use different virtual machines.
- The type of ledger – UTXO or account based.
- Token economics – Is the cryptocurrency minable? Do users need to pay a fee for transactions?
Different blockchain projects use a different set of combinations from the options above to create their network. The specific combination used is dependent on the needs of the project and the future direction they wish to take.
The problem is that it becomes extremely difficult when one of these components becomes outdated and needs to change. For example, Ethereum has been wanting to change to PoS for a long time, and this is proving to be very difficult to achieve while the blockchain is still live and running.
Taking the Ethereum example one step further, let us imagine if PoW or PoS were to become completely obsolete with the invention of a new a consensus mechanism (let us call it Superior PoS-2.0, or s-PoS-2.0). In this case, the majority of our favorite cryptocurrency projects would be left scrambling as they struggle to implement the latest consensus mechanism.
This would, in turn, create a wave of new hard forks as projects across the entire industry need to implement the latest tech while their blockchains are still running. However, if the projects had been built on an adaptable infrastructure which was actively was building toward the future, they could simply implement the changes on a new shard and seamlessly transition to the latest tech with ease.
This example is not strictly limited to a change in the consensus mechanism. If any of the components mentioned above were to be changed, this would create severe problems for our favourite blockchains to be able to adapt to. If the transaction model or token economics were changed, this would also lead to a struggle amongst our favorite blockchain projects to implement the latest tech.
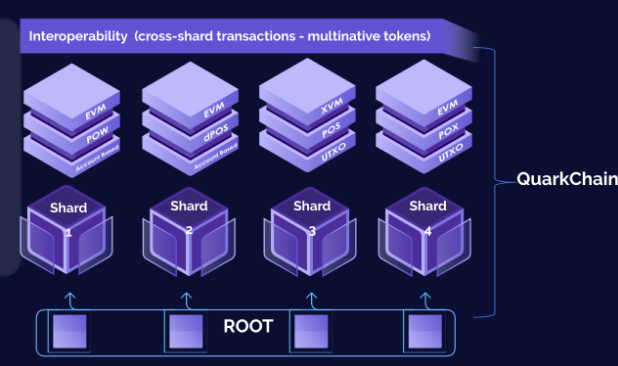
For QuarkChain 2.0, each shard can be customized for any combination of the components mentioned above. QuarkChain 2.0 will be the first project enabling multiple consensus mechanisms, multiple transactional models (including multiple virtual machines), multiple ledger types, and multiple token economics to all exist together on the same infrastructure.
This presents a unique opportunity for businesses that wish to enter the blockchain space. Businesses can now select a unique combination that is specific to their needs, while simultaneously enjoying the scalability and security brought by QuarkChain.
Benefits of Having a Blockchain Infrastructure Such as QuarkChain 2.0
The introduction of QuarkChain 2.0 brings a whole range of benefits that can be enjoyed by project leaders and the overall community alike.
The Problem of Hard Forks
One of the first benefits to highlight is in relation to hard forks. Over the years, we have seen many hard forks occur within our favorite cryptocurrencies. Bitcoin forked off into Bitcoin Cash and later into Bitcoin SV. Ethereum forked off into Ethereum Classic after the notorious hack that occurred on the Ethereum blockchain. Each of these hard forks came about due to differences in technology opinions amongst the crypto’s community.
The destruction toward a blockchain’s community is apparent after a hard fork occurs. The community splits as different investors gravitate to the future roadmap that they deem has the most potential. The damage to the project extends not only to the dilution of hashing power, but also into the volatility of market prices before and after each hard fork. However, the QuarkChain 2.0 infrastructure can help combat hard forks within projects, as it allows different technologies to exist within the same infrastructure.
Highly Customizable
Another benefit for businesses building on QuarkChain is the option for them to create a highly customized token that is specifically set for their purpose. For example, a decentralized exchange will require order book information to be embedded into the ledger, while other companies may not. Games will prefer dPoS consensus mechanisms due to the low confirmation times. Projects can choose to plug into the Ethereum Virtual Machine, the Tron Virtual machine, or any other Virtual Machine in existence.
All of this means that businesses can use QuarkChain 2.0 to build the perfect technology blockchain for their specific purpose, without having to bend to the rules that other blockchain infrastructures set.
A Real Native Token
Perhaps one of the most important benefits to running a project on QuarkChain 2.0 is the fact that the token generated by the QuarkChain blockchain will be its own native token. This means it will not be a derivative of the main token, such as an ERC-20 token for projects built on Ethereum, or a TRC-10 token for projects built on Tron. This feature allows projects to build their own token economics without having to feed the mainchain tokens in gas fees, such as with ETH and NEO.
Building For the Future
Another extremely important benefit of QuarkChain 2.0 will be the fact that they are building for the future. When they say that their infrastructure is flexible, they mean it. As blockchains evolve, technology emerges that presents new, unique opportunities for projects. Whether an emerging technology be a new consensus protocol or a new virtual machine, QuarkChain 2.0 can easily integrate it with as little friction as possible.
Reaching the Singularity
The QuarkChain Mainnet V1.0 is officially live as of April 30 2019, and has been dubbed as Singularity. The Mainnet chain aims to provide a better solution for the blockchain trilemma where QuarkChain has found a balance between maintaining decentralization, scalability, and network security at the same time. Furthermore, the Mainnet provides a blockchain that is extremely flexible towards the future and is highly interoperable.
The team suspect that the Mainnet token swap will occur after the Mainnet has been running stable for at least 3 months.
Conclusion
QuarkChain is making considerable progress toward their goal of building a highly flexible, scalable, and user-orientated blockchain infrastructure by implementing sharding technology.
Nobody really knows what will happen to the evolution of blockchain. With different consensus mechanisms and a range of virtual machines, it is difficult to estimate which will be the most successful and which will fail and crumble.
However, the infrastructure provided by QuarkChain 2.0 provides blockchain projects security against the constant evolution of the technology. Their team has built an infrastructure that allows for the customization of each project according to its needs, while maintaining the option to remain future-proof, as new technologies can be implemented within the infrastructure with ease.