Ethereum was developed to be a smart contract platform for dapps. Other smart contract platforms began to rise after Ethereum, with proposed solutions to some of the challenges Ethereum has.
Metaverse, based in Shanghai, is a decentralized platform for smart properties. It is developed by ViewFin Corp, structured to compete with NEO, Ethereum, and other blockchain platforms, but it is not as heavily publicized. It is also known as a Chinese alternative to Ethereum.
The goal of Metaverse is to create a new reality where digital assets and digital identities build the basis for asset transaction. Metaverse envisions a future where the world transitions from an internet of information to an internet of value, and digital asset transfers take place on the blockchain through digital identities and value intermediaries.
What Does Metaverse Do?
The Metaverse blockchain’s chain of operation, according to their whitepaper, is illustrated below. The left side represents other smart contract blockchain platforms while the right side represents Metaverse.
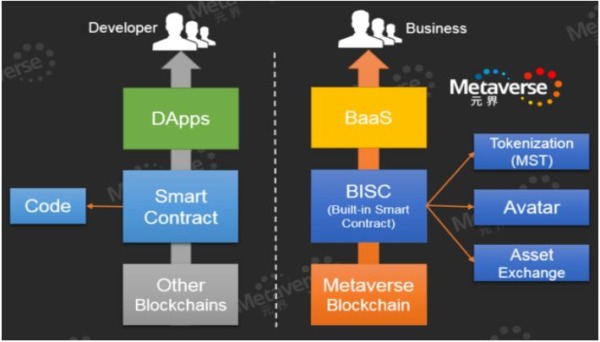
The service rendered by Metaverse can be classified into 4 categories:
- Digital assets (represented by their token MST)
- Digital identities (referred to as Avatars)
- Oracle intermediaries
- On-chain exchange
Metaverse Smart Token
Metaverse tokenizes smart contracts using the Metaverse Smart Token (MST).
MST is basically a digital asset represented on the Metaverse blockchain. Digital assets (via the MST) are trust-free, traceable, and decentralized smart properties that can be freely registered, transferred, issued, deposited, used as collateral, and burnt.
Metaverse Avatar
Ownership of digital assets is controlled by individuals on the Metaverse blockchain through digital identities.
The Metaverse Avatar is a digital identity solution on the Metaverse blockchain where various pieces of relevant information will be attached to each avatar’s unique index and encrypted for data privacy. This will allow digital asset interactions with other identities.
Metaverse Oracles
Metaverse makes use of trusted intermediaries to verify the reliability of information processed on the blockchain. An oracle is a position reserved for a “middleman” on the Metaverse blockchain. An oracle is a special type of avatar based on the avatar’s authentication and authorization. Anyone can be an oracle but the credibility of the oracle will be based on their record and reputation.
There are various types of oracles on the Metaverse blockchain. Host oracles can store physical assets and issue smart assets on the blockchain. Authentication oracles provide proof of personal information and correlation with avatars. Supervision oracles provide transaction authenticity or proof of compliance for transactions.
There are other types of oracles that function on Metaverse, bringing speed and transparency to the network.
On-Chain Exchange
Metaverse also carries out an on-chain exchange, allowing value to be exchanged freely and easily, with control staying in the hands of the users.
Metaverse not only provides a platform for decentralized applications, but it supports centralized, human-controlled applications as well. Also, Metaverse provides BaaS service (Blockchain as a Service), allowing services provided by the blockchain platform to be conveniently integrated into existing internet applications and services.
Consensus
Metaverse currently functions on a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism. However, based on the plan of the blockchain platform, it will not always be PoW.
The development of the platform comes in 2 stages. The first stage has a PoW consensus model to grow the ecosystem, but as the mining rewards near its limits, the consensus model will switch to a form of Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS).
The PoW consensus currently in use is Ethash. The development team is working on a special modification of the DPoS to tackle the flaws of the model known as HeartBeat Token-Height Delegated Proof of Stake (HBTH-DPoS).
Metaverse’s History and Team
The name “Metaverse” was inspired by the 1992 science fiction novel Snow Crash, as the change the internet brought is quite similar to the circumstance of events in the book. Inspired by the novel’s depiction of avatars communicating with each other in a virtual-reality realm, Metaverse envisions bringing a new reality and shaping a new economic model through the internet of value.
Eric Gu (founder and CEO of Metaverse) was working on NEO (he was on the founding team) before starting Metaverse. He has extensive programming experience working in US and Canada, and is also the CEO of Viewfin Corp. In 2016, Gu founded Metaverse along with Chen Hao, who now acts as CTO. They work alongside a team of engineers and managers, operating in Shanghai, China.
The blockchain launched in February 2017 after 2 successful ICOs — one in September 2016 and one just before the mainnet launch in February 2017 — that together sold 50 million tokens.
Achievements and Roadmap
The Metaverse mainnet was launched in February 2017. On June 6, 2018, the Supernova, an upgrade of the Metaverse blockchain, was released on the mainnet according to the roadmap. This upgrade included a full-node wallet. The next upgrade is known as Pillars, which is expected to be on the mainnet by March 2019.
On August 13, 2018, Metaverse announced their most recent partnership. Lexit, a digital M&A marketplace, has agreed to team up with Metaverse to transform how intellectual property (IP) is transacted. This partnership can be viewed as a cooperative initiative to tokenize intellectual property.
Other notable partnerships of Metaverse include with trade.io, Zhejiang University (to co-establish a Blockchain Technology Laboratory), and AION. Dapps being developed on Metaverse include Luxchain, ParcelX, and LeBlock.
A partnership that shows a great deal of promise is that of startup Zengold, which is digitizing gold using the Metaverse blockchain, thereby enabling the transaction of the asset while the ownership information is kept secure on the blockchain.
The Metaverse roadmap for 2018 and Q1 2019 is shown below.

How to Buy and Store the ETP Token
The native token of the Metaverse blockchain is known as Entropy (ETP).
ETP is a utility token. It is the cryptocurrency in which miners and developers are rewarded on the blockchain. It can also be used as a collateral in the blockchain ecosystem. Transaction fees will be charged in ETP for various transactions on the network.
The Metaverse Smart Token (MST) is issued freely by users of the blockchain, and its value can be measured in ETP. The Metaverse Smart Token (MST) is not a cryptocurrency in itself; rather it is the form digital assets take on the Metaverse blockchain.
ETP can be purchased with Bitcoin and Ether on exchanges such as Bitfinex, HitBTC, and Coinsuper. ETP can be purchased with USD on Bitfinex.
ETP can be mined like any PoW coin. It currently has a total supply of about 56 million, with about 44 million tokens yet to be mined. The maximum supply of tokens is 100 million. With the current total supply at about 56 million, over 53 million ETPs are already in circulation.
ETP can be stored in the Metaverse wallet. The wallet has a desktop version, a mobile version for both Android and iOS, and a web version. No hardware wallets currently support ETP. At the moment, the Metaverse wallet is the only place to store your ETP tokens after taking them out of an exchange.
Challenges and Competitors
In the sphere of blockchain platforms, partnerships matter because there is no point building a network that nobody is using. Every blockchain platform has the challenge of attracting users and developers to their platform. Although Metaverse has not made many loud partnerships, some find its method of gradual and “silent” progress appealing.
As a platform for smart contracts and dapps, Metaverse competes with the vast number of the blockchain projects offering the same service. Notably, Ethereum and NEO are close competitors, but others such as EOS and Qtum can be considered competition as well.
Conclusion
Metaverse is unique in its approach to BaaS. While that is an edge over other platforms, it is only valuable when there are individuals and organizations that use the platform.
Metaverse still has a lot further to go before it shakes the standing of the big names in blockchain smart contract platforms.
However, with the beginnings of a solid ecosystem in the making, they are on their way. They may still be flying below the hype radars, but their potential for real-world projects is very appealing, especially considering their partnership with Zengold.