There are over 2,000 cryptocurrencies today. Many people who own one cryptocurrency will desire to exchange it for another. This gave rise to crypto exchanges. And yet, even though there are currently over 200 crypto exchanges in the world, users still have challenges exchanging one cryptocurrency for another.
Centralized crypto exchanges (such as Binance and Huobi) are currently the most common, and are more suitable for professional traders. However, for day-to-day users who desire to exchange their cryptocurrency to make a payment, centralized exchanges are not so effective for that. Aside from the hacks and fees, the transaction process is long and it can trigger mistakes by the user.
Decentralized crypto exchanges often have the problem of liquidity and orders may not be filled as promptly as the user needs it. This is the reason behind the user-oriented exchange network that facilitates the seamless exchange of tokens, especially for payment purposes.
Kyber Network is an Ethereum-based protocol that allows instantaneous exchange and conversion of cryptocurrencies (both coins and tokens) with high liquidity, without the order book. This is similar to the 0x protocol, the major difference being that the Kyber Network does its exchange on-chain.
What Does the Kyber Network Do?
Kyber Network allows the transfer and exchange of cryptocurrencies peer-to-peer. This means that a sender can send ETH and the receiver receives another cryptocurrency.
Assume a seller accepts ETH for payment in a store. A buyer who wants to carry out a transaction only has BAT. The seller doesn’t accept BAT. So, instead of exchanging the BAT to ETH and then send the payment to the seller, the transaction can be carried out in one smooth go on the Kyber Network.
On the Kyber Network interface, let’s say the buyer sees that 782 BAT equals 1 ETH. The buyer then enters a request on Kyber to send 782 BAT worth of ETH to the seller. The Kyber Network has a reserve of digital assets to maintain exchange liquidity for every transaction. The Kyber smart contract then confirms the buyer has enough BAT for the conversion.
Upon approval, the contract sends 1 ETH to the seller and it will appear to the seller that the funds came directly from the buyer.
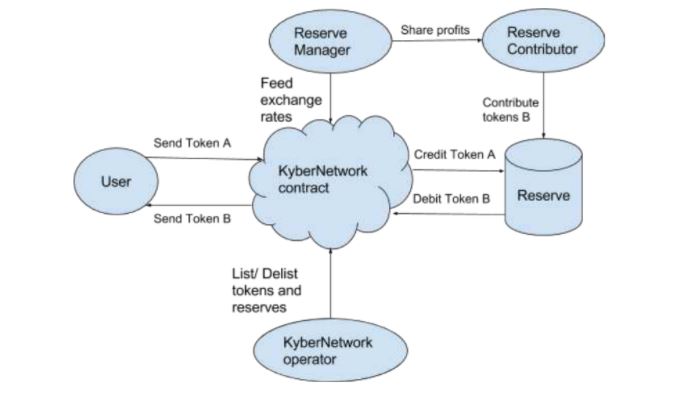
Kyber Network Stakeholders
The Kyber Network ecosystem consists of the following stakeholders:
- Users which send and receive tokens to and from the network. They could be individuals, merchants, or smart contract accounts.
- Reserve Entities which function as a source of liquidity to the platform. They can be internal or hosted by a registered third party. If the public contributes to the reserve, it is considered a public reserve. If not, it is private.
- Reserve Contributors which are individuals that provide funds for public reserve entities to increase liquidity. They share in the profits from the reserve.
- Reserve Managers which maintain the reserve, determine the conversion rates of the digital assets in their reserve and feed it into the network.
- Kyber Network Operators which add or remove Reserve Entities and control which tokens are listed. This role is played by the Kyber team for the beginning stages, but eventually, it will be switched to a decentralized governance.
The interaction of the different stakeholders in the Kyber Network is illustrated as shown below.
Dynamic Reserve Pool
Liquidity is maintained in the Kyber Network through dynamic reserve pool. The Kyber Network allows the entrance of multiple reserve entities. This makes sure that there are no monopolies and the conversion rates stay competitive. Having multiple reserve entities also allow tokens with low trading volume to become listed on the network, as Kyber reserves might not list them.
The Kyber smart contract makes sure that the user gets the best conversation rate by considering all the reserves that can process the request.
Kyber Network protects the system from bad actors by flagging any exchange rate that is extraordinarily out of the norm. The management model of funds is made straightforward and transparent to protect public reserve entities.
Reserve managers can earn profits through the spreads set for their reserves.
History of Kyber Network
The CEO of Kyber Network, Loi Luu, conceived the Kyber Network as a “decentralized version of Shapeshift.”
On August 7, 2017, a sample of the Kyber smart contract and electronic wallet was posted as a minimum viable product.
The token sale took place September 15-17, 2017. The ICO raised 200,000 ETH, making it one of the largest ICOs in 2017.
The Kyber Network Team
Kyber Network is led by its founders Loi Luu (CEO), Yaron Velner (CTO), and Victor Tran (Head of Development).
The team consists of consists of developers, managers, engineers, and designers based in Singapore.
The Kyber Network is further strengthened as a project in the crypto community with the famed co-founder of Ethereum Vitalik Buterin being one of the advisors.
Kyber Network Roadmap and Achievements
On February 10, 2018, Kyber Network was launched on the mainnet. The network started by supporting exchanges between ERC-20 tokens and ETH, with the internal team’s reserve entity serving almost all trades.
The Kyber Network has secured a wide range of partnerships with other crypto projects. A few of them include Trust Wallet, Icon, Storm, Request Network, MyEtherWallet, Coinmanager, and Toshi.
In Q2 2018, Kyber Network announced support for ERC-20 token to ERC-20 token conversion.
The roadmap which highlights the future direction of the Kyber Network is illustrated below.


Competitors
The closest competitor of Kyber Network is the 0x protocol. Centralized and decentralized exchanges can also be referred to as competitors. Although the Kyber Network was envisioned as a “decentralized Shapeshift”, Shapeshift can also be considered one of its competitors.
Aside from the big difference between Kyber (on-chain) and 0x (off-chain), liquidity is guaranteed on Kyber Network, unlike 0x. Moreover, trades are instant on the Kyber Network, unlike 0x.
The Kyber Network Token (KNC)
The Kyber Network Crystal (KNC) is an ERC-20 token required for reserves to participate in the network and reward parties that help generate more trading activities on the platform.
Third-party reserves are required to purchase KNC to pay for their operation. Dapp platforms integrated with Kyber’s API will receive referral fees in KNC. Network fees on Kyber are charged in KNC and a portion of this received fee is burned.
The total supply of KNC tokens is about 215 million, with about 134 million tokens currently in circulation. The coin is currently priced at about $0.40, having reached an all-time high of $5.80 in January 2018.
KNC can be bought on Binance, Huobi, Bithumb, OKEx and, of course, on the Kyber Network itself.
KNC tokens can be stored in any ERC-20 compatible wallet.
Conclusion
There are already several ways to exchange or trade one cryptocurrency for another. Kyber Network creates a way to make the exchange in a very applicable way to users guaranteeing liquidity and instant transactions without being centralized.
As Kyber Network grows and achieves cross-chain interoperability, the platform will become more relevant even as cryptocurrencies gain mainstream adoption. No crypto exchange project has a monopoly on the market and this is a good thing.
Developments in Kyber Network, and its direct and indirect competitors, will likely keep the crypto world interesting.